Table Of Content

Complicated data relations also slow down querying and negatively affect performance. PostgreSQL retains a high level of performance and flexibility, even when handling large databases. It's the right choice for users that need high read/write speeds and extensive data analysis. Illinois Tech is a top-tier, nationally ranked, private research university with programs in engineering, computer science, architecture, design, science, business, human sciences, and law.
Foreign key
The double lines indicate total participation, which means every entity in the table must participate in the relationship — in our case this means every course must have a teacher. The single lines indicate partial participation, so in our case there may exist some teachers who are not yet or not currently teaching any courses. Here is a slightly longer explanation of this distinction if you would like to read some more. Our next step is to think about which attributes we want to store for each of our entities. This may be spelled out in detail in our requirements document, or it may require more discretion on the part of the database developer.
Making a plan based on the requirements
For example, the section on normalization and how to progress through the different forms/stages is not exactly correct. Specifically, the book gives an incomplete definition of normalization, and the example of 1NF shows the wrong primary key. In addition, the figures in the book link to other unrelated figures when you click them to get a closer look. At this point, we’ve discussed all the major components of database design in DBMS tutorials. It’s crucial to understand that database design isn’t just a one-off process; it’s an ongoing cycle that requires careful planning, implementation, and maintenance. It’s a process that requires patience, practice and a lot of learning-by-doing.
Composite key diagram:
It also limits the maximum size of the database to 32,000 columns and 140 TB. MariaDB builds upon the MySQL base by adding support for even more storage engines and fixing storage engine limitations. This allows it to perform even faster than MySQL and run both SQL and NoSQL in a single database.
In sum, this textbook is a good resource for new learners in the topic of Database design/management. The resolution of included figures is not high enough to be clearly displayed. Furthermore, when clicked, image with same resolution or even the wrong image was displayed which couldn't address the issue of pdf version.
The flow of the book is very good and follows the state of the art for other very well know references in the same field. The text is easy to read and easy to divide in smaller sections that can be assigned within the course. The examples in the book are general and diverse and to my knowledge should not be offensive to any community. There were no major interface issues encountered while using this book. Figures and charts were blurry in some places and the distortion in size made it somewhat difficult to read those portions without interruption.
Referential Integrity
A glossary is available for quick reference to key terms used throughout the module. In this module, you will learn about the fundamental aspects of MySQL and PostgreSQL and identify Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) tools. You will explore the process of creating databases and tables and the definition of keys, constraints, and connections in MySQL. Additionally, you will discover important processes in PostgreSQL using command line, pgAdmin, and views.
non-relational databases
Although relational databases quickly grew in popularity, a few of the relational model’s shortcomings started to become apparent as data became more valuable and businesses began storing more of it. For one thing, it can be difficult to scale a relational database horizontally. Horizontal scaling, or scaling out, is the practice of adding more machines to an existing stack in order to spread out the load and allow for more traffic and faster processing.
Relations that store data are called "base relations", and in implementations are called "tables". Other relations do not store data, but are computed by applying relational operations to other relations. Derived relations are convenient in that they act as a single relation, even though they may grab information from several relations. However, it utterly fails to address the cultural contexts of data within organizations and society.
It shares some features with MySQL, with the notable addition of MVCC (multi-version concurrency control), making it ACID compliant. Our database might have a table containing customer information, with columns representing customer names or addresses, while each row contains data for one individual customer. On the other hand, NoSQL databases don't need to rely on structure as much, which allows them to store large amounts of data, remain flexible, and easily scale storage and performance. The relationship between the Customers and Orders tables is a one-to-many relationship, which means that one customer can place multiple orders, but each order can only belong to one customer. This is indicated by the line connecting the tables with a 1 on one end and a N on the other end. The materialized view is created by selecting data from one or more base tables in the Master Site and storing them in a new table in the Materialized View Site.
It can improve the performance of queries that use the same subquery results repeatedly, or that are complex or run on large data sets. A materialized view is updated automatically or on demand when the source data changes, so it always reflects the current state of the data. A materialized view is a type of cache that can be disposed and rebuilt from the source data. Make sure that you fully aware of it, develop programming logic to handle it, and properly document the decision.
Exploring Database Schemas. A Journey from Basic Types to Advanced… by Rudresh Narwal 👨💻 - Medium
Exploring Database Schemas. A Journey from Basic Types to Advanced… by Rudresh Narwal 👨💻.
Posted: Mon, 08 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
But to use relational databases well, you need to follow some patterns that solve common problems and make your data work better. In this article, we will look at different patterns for relational databases, and explain how they can help you with specific issues and improve your database performance. This conceptual article outlines the history of the relational model, how relational databases organize data, and how they’re used today.
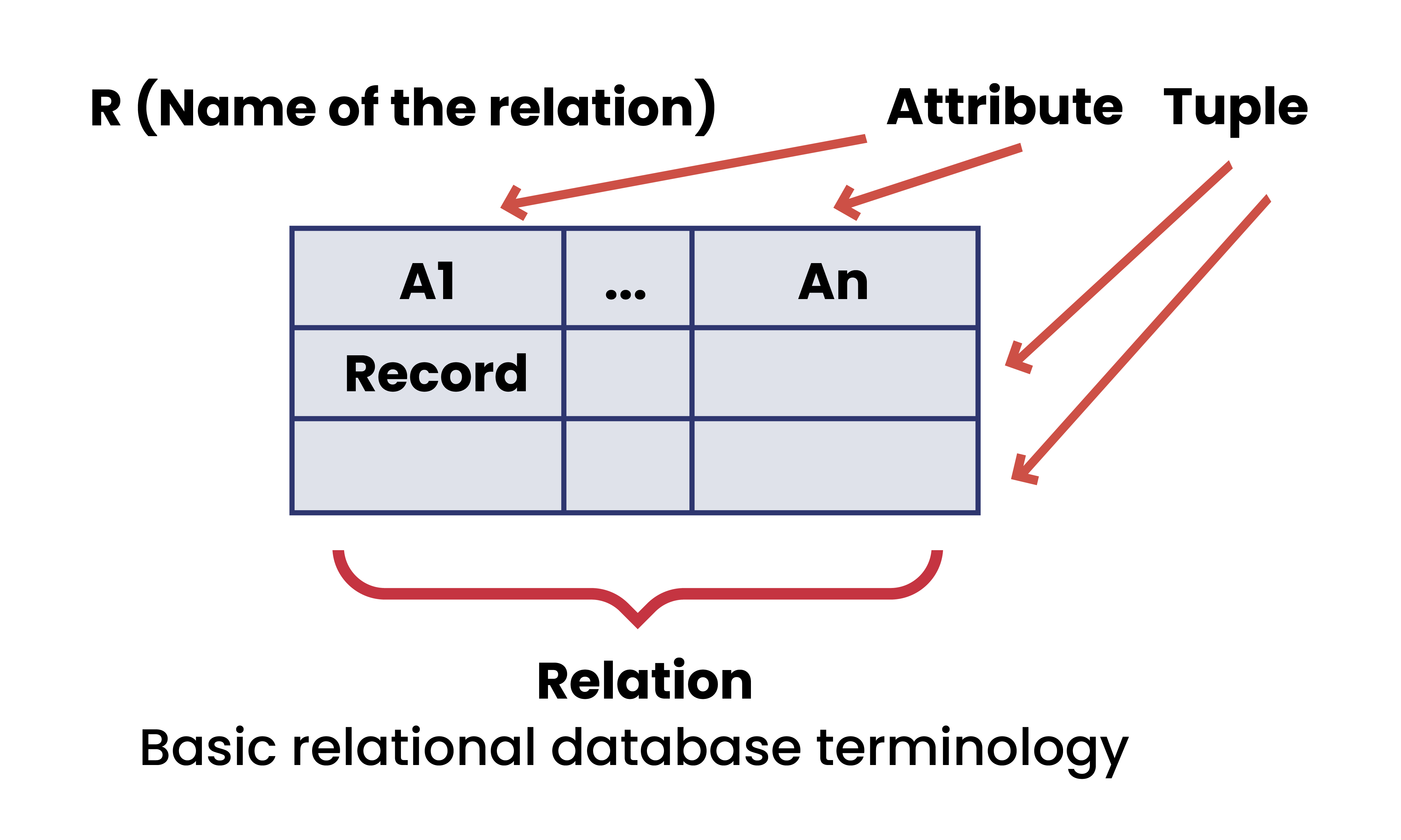
A relational database consists of a collection of tables, each of which is assigned a unique name. Consider a relation STUDENT with attributes ROLL_NO, NAME, ADDRESS, PHONE, and AGE shown in the table. Structured Query Language — commonly known as SQL — is a language used to define, control, manipulate, and query data held in a relational database. SQL has been widely adopted since it was first developed in the 1970s, and today it’s the predominant language used to manage relational database management systems. Quite the contrary, the relational model is still the dominant framework for data management after over 40 years.
Beginners to database design frequently fail to understand the impact that database structure can have on the structure and function of an organization. Sometimes organizations find themselves having to adapt to their data structures rather than the other way around. It is now generally recognized that gender is a non-binary facet of identity. An otherwise well-meaning developer who reduced gender to "male/female" may cause unintended harm to the people whose data is being stored in a database. The traditional failure of the software community to consider, let alone address, issues like this is replete through the industry.
The materialized view can then be queried like a regular table, without having to access the base tables every time. The materialized view can also be refreshed periodically or on demand, to reflect the changes in the base tables. Suppose we have a table called vehicles that stores information about cars, trucks, and motorcycles. We can use STI to store all the vehicles in one table, with a column called type that specifies the subclass of each vehicle.
When a new row is written to the table, a new unique value for the primary key is generated; this is the key that the system uses primarily for accessing the table. Other, more natural keys may also be identified and defined as alternate keys (AK). Often several columns are needed to form an AK (this is one reason why a single integer column is usually made the PK). Both PKs and AKs have the ability to uniquely identify a row within a table. Additional technology may be applied to ensure a unique ID across the world, a globally unique identifier, when there are broader system requirements. Today, autonomous technology is building upon the strengths of the relational model, cloud database technology, and machine learning to deliver a new type of relational database.

No comments:
Post a Comment